Microalgae, an innovative solution for decarbonising industry
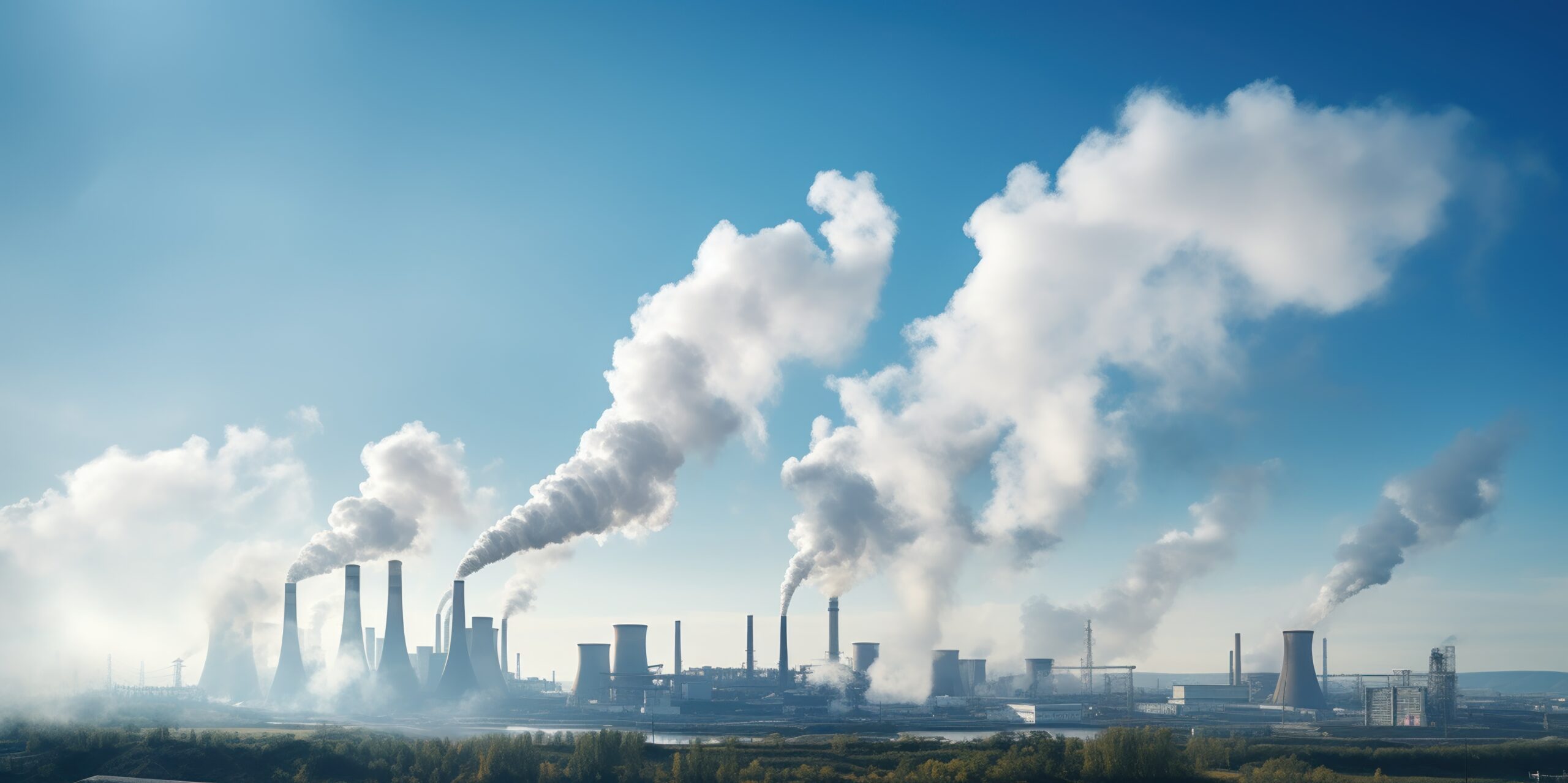
As part of global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat global warming, decarbonising industry is a major challenge. Microalgae, microscopic photosynthetic organisms, represent an innovative and promising solution for capturing CO2 and recovering it in a sustainable way.
Thanks to their capacity for photosynthesis, microalgae can absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. This action is even consubstantial with their development process: during their growth, they use CO2 as a raw material to produce biomass, in particular lipids, proteins and carbohydrates. This process of capturing and transforming CO2 into biomass makes microalgae an effective way of reducing CO2 concentrations in the air. In addition, these organisms can grow in controlled environments, such as photobioreactors, where the air is directly enriched with CO2 to optimise their growth.
Combining this capture technique with recovery processes offers considerable potential. The algal biomass generated can be transformed into a variety of high added-value products, including molecules of interest, biofuels, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and fertilisers. These applications make it possible to close the carbon cycle by reusing biomass for industrial and energy purposes, while reducing dependence on fossil resources.
In addition, microalgae have the advantage of being able to be grown on non-arable land or in brackish water, thereby limiting competition with agricultural land. In this way, they can contribute to a circular economy model, where the decarbonisation of industry goes hand in hand with the development of renewable resources.
In short, microalgae offer a dual solution: efficient capture of CO2 and industrial recovery that could play a crucial role in the energy transition and the decarbonisation of industry.
More news News